 |
LibrePCB Developers Documentation
|
 |
LibrePCB Developers Documentation
|
This page is aimed both at developers as well as packagers. If you're a packager and have any question regarding the LibrePCB build system, please join our chat or forum!
If you want to contribute a new feature or a bugfix to LibrePCB, the best way is to use Qt Creator. To get started, simply open the top-level CMakeLists.txt file with Qt Creator.
When opening a project in Qt Creator for the first time, you need to configure the Desktop kit:
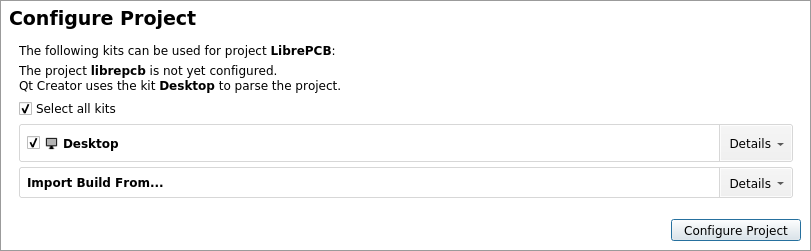
Click on the "Configure Project" button to get started.
Select the run configuration librepcb and click on the Run button:
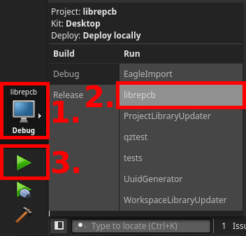
If ninja is installed on your system, Qt Creator will use it by default, resulting in parallel builds (utilizing all your CPU cores) out of the box. If the fallback to GNU Make is being used, you may need to set make flags in order to achieve parallel builds.
You can also build LibrePCB from the command line using cmake:
mkdir build && cd build cmake .. make -j8
Then run the librepcb binary in the build/apps/librepcb/ directory.
To install LibrePCB on your system, run make install.
If you regularly rebuild parts of LibrePCB, you can speed up that process by installing ccache and passing -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_LAUNCHER=ccache to CMake.
cmake .. -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_LAUNCHER=ccache
By passing in the CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX parameter, you can change the install prefix. For example, if you want to install LibrePCB to /usr/local, use
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local
By default CMake will create a release build without debug symbols.
To customize the build type, pass the CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE parameter to CMake. For example, to create a debug build:
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
Available build types:
Debug: Debug buildRelease: Standard release buildRelWithDebInfo: Release build with debug symbolsMinSizeRel: Release build optimized for minimal sizeBy default, our own libraries and applications are compiled with -Wall. If you want to treat warnings as errors (advisable in CI, or before committing), pass the BUILD_DISALLOW_WARNINGS parameter to CMake:
cmake .. -DBUILD_DISALLOW_WARNINGS=1
For investigating bug reports, it's useful to know where the application binary is coming from. Therefore this information can be compiled into the executable with the LIBREPCB_BUILD_AUTHOR parameter. Its value is then shown in the "About LibrePCB" dialog.
cmake .. -DLIBREPCB_BUILD_AUTHOR="Flathub Buildbot"
The share directory contains icons, fonts, templates and more resources that LibrePCB needs at runtime. On a Linux system, it is usually located at /usr/share/librepcb.
By default (unless LIBREPCB_REPRODUCIBLE is set), the build process will embed the absolute path to the share directory located within the source tree into the binary. When starting LibrePCB, it will first check whether the binary is running from within CMAKE_BINARY_DIR. If that is the case, the share directory in the source tree will be used. Otherwise, LibrePCB will fall back to ../share/librepcb relative to the application binary.
This will work out-of-the-box in many cases. However, when packaging LibrePCB, you should explicitly set the share directory path (either an absolute or a relative path).
cmake .. -DLIBREPCB_SHARE=/usr/share/librepcb
So far, LibrePCB does not officially support reproducible builds. However, we allow turning off some features that make the binary non-reproducible (like embedded source directory paths, or embedded git commit hashes). This should make it easier to achieve reproducible builds in the future.
cmake .. -DLIBREPCB_REPRODUCIBLE=1
The OpenGL Utility Library (GLU) is needed for the 3D viewer of LibrePCB and thus needs to be available both at built time and runtime. If this library is not available for a particular platform, it is possible to compile without it but the 3D viewer won't render all layers then.
cmake .. -DUSE_GLU=0
Parts of the 3D features (e.g. reading/writing STEP files) depend on the OpenCASCADE library, also known as OCCT or OCE. As this library might not be available on any platform, or might lead to packaging issues, it is possible to build LibrePCB without these 3D features. The OpenCASCADE dependency is then not needed, while LibrePCB is still usable without any issues, just without full 3D support.
cmake .. -DUSE_OPENCASCADE=0
We recommend using the official OpenCASCADE library (OCCT), but generally LibrePCB should also work with the Community Edition (OCE). CMake should automatically detect the availability of both variants.
By default, all dependencies except Qt and OpenCascade will be linked statically using vendored git submodules. If you prefer to unbundle some libraries, set the UNBUNDLE_xxx variable:
cmake .. -DUNBUNDLE_FONTOBENE_QT=1 -DUNBUNDLE_POLYCLIPPING=1
To unbundle all dependencies that support it, use -DUNBUNDLE_ALL=1.
Right now, the following libraries can be unbundled:
| Library | Parameter | Search Methods |
|---|---|---|
| dxflib | UNBUNDLE_DXFLIB | pkg-config |
| fontobene-qt | UNBUNDLE_FONTOBENE_QT | pkg-config, find_path |
| googletest | UNBUNDLE_GTEST | cmake, pkg-config |
| muparser | UNBUNDLE_MUPARSER | cmake, pkg-config |
| polyclipping | UNBUNDLE_POLYCLIPPING | pkg-config |